end tidal co2 range high
The presence of a normal waveform denotes a patent airway and spontaneous breathing. An increase in etCO2 by 5 appears to have reasonable sensitivity 71-91 and specificity 94-100 for fluid responsiveness in two studies of patients breathing passively on the ventilator.

Pre Hospital Capnography Ppt Download
High VT and low resp rates.

. The number is called capnometry which is the partial pressure of CO 2 detected at the end of exhalation ranging between 35 - 45 mm Hg or 40 57 kPa. Measuring end-tidal CO2 in cardiac arrest patients is helpful for confirming tracheal tube placement assessing the effectiveness of chest compressions predicting likelihood of return of spontaneous circulation ROSC in that a persistently low ETCO2 tends to predict death whereas a high or rising ETCO2 is associated with a higher chance of ROSC. There was no significant change in EtCO2 after treatment.
ETCO2 emergency department monitoring and critical. End-tidal capnography or end-tidal CO2 EtCO2 monitoring is a non-invasive technique that measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide CO2 at the end of an exhaled breath. The median EtCO2 at T0 and T60 was 35 IQR.
The end-tidal carbon dioxide tension PetCO2 measured after a single large tidal-volume breath 15 mlkg body weight was compared to simultaneous measurements of PaCO2 in 6 dogs with normal lungs who were receiving high-frequency jet ventilation HFJV. The median initial PEFR was 200 interquartile range IQR. In conditions of normal breathing 6 Lmin 12 breathsmin 500 ml for tidal volume etCO 2 is very close to alveolar CO2.
There was an excellent linear correlation b. The normal values are 5. The amount of CO2 at the end of exhalation or end-tidal CO2 ETCO2 is normally 35-45 mm HG.
Norm al EtCO2 levels 46 to 60 kPa signify adequate perfusion. The height of the ETCO2 waveform during CPR has been used as an indirect measure of adequate chest compressions helping those involved in resuscitation monitor the effectiveness of their compressions in real time. End-tidal CO2 may be useful here as an easily and immediately measurable index of changes in cardiac output.
78 Nitrogen 21 Oxygen 1 CO2 and other gases Exhaled gases. From 2000 to 5000 ppm CO2 concentration starts to cause problems headaches insomnia nausea. 21 Hillier SC Badgwell JM Mcleod ME Creighton RE Lerman J.
The height of the capnography waveform accompanies this number on the monitor as well as the. From 5000 ppm the presence of other gases in air is altered arising a toxic atmosphere or poor in oxigen with fatal effects as the concentration increases. Where the respiratory rate is very low and the tidal volumes are very large the end-tidal CO 2 can be higher than the mean arterial CO 2.
Capnograph is an indispensable tool for monitoring metabolic and respiratory function. Waveform and end -tidal carbon dioxide EtCO2 values. There was no significant change in the Q angle and the T time after treatment.
It is a dirty air. Accuracy of end-tidal PCO2 measurements using a sidestream capnometer in infants and children ventilated with the Sechrist infant ventilator. NaHC03 will increase EtCO2 because it splits into CO2 and H20 So if rises after NaHCO3 do not misinterpret as ROSC Vasopressors will decrease ETCO2 they cause high afterload increasing BP and myocardial blood flow but a decrease in cardiac output.
Between 35 and 45 Remember a normal end-tidal is between 35 and 45. In fact its commonly called the ventilation vital sign. In the awake adult normal cardiac index lies between 25-4 Lminm2 with an ETCO2 of 35-45 mmHg.
Capnography waveforms etCO2 and breathing patterns. Utility of end-tidal carbon dioxide detector during stabilization and transport of critically ill children. In normal conditions CO2 is 5 to 6 which is equivalent to 35-45 mmHg.
Monitoring of end-tidal carbon dioxide EtCO2 is a noninvasive method that measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide CO2 at the end of exhaled breath which is expressed as a percentage of CO2. Guide to End Tidal CO. Most anesthetics are respiratory depressants and end-tidal CO2 allows early detection of respiratory impairment so appropriate intervention can occur before the.
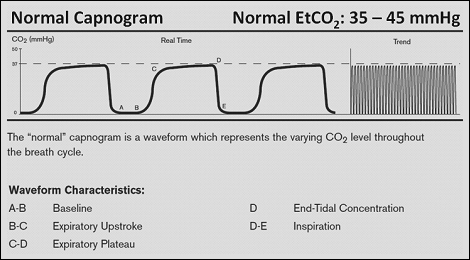
End Tidal CO 2 sampling Ventilatory function minute ventilation decreases and therefore CO2 increases in a A dead space gasno CO2 B mixed gasrising CO2 C alveolar gasCO2 plateau D inspiration no CO2 The monitor will continuously read the CO2 level in or mm Hg and display the peak CO2 value ETCO2 and respiratory rate. Total pressure of a gas is the sum of the partial pressures of the gas Expired CO2 measured PetCO2 mmHg in waveform Percentage Normal Levels PaO2 85-100mmHg PaCO2 35-45mmHg Percentage vs. 30-38 and 34 IQR.
End Tidal CO 2 6 Can also be measured and monitored in spontaneously. End-tidal carbon dioxide measurement allows non-invasive measurement of the ability of the respiratory system to excrete carbon dioxide usually indicative of respiratory function. Monitoring of end-tidal carbon dioxide EtCO2 is a noninvasive method that measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide CO2 at the end of exhaled breath which is expressed as a percentage of CO2.
The waveform is called capnograph and shows how much CO 2 is present at each phase of the respiratory cycle. What should end-tidal volume be. It consists of a number and a graph.
Capnography can be used to assess unresponsive patients ranging from those are actively seizing to victims of chemical terrorism. The number is capnometry which is the partial pressure of CO2 detected at the end of exhalation. End-tidal carbon dioxide ETco 2 monitoring provides valuable information about CO 2 production and clearance ventilation.
In normal conditions CO2 is 5 to 6 which is equivalent to 35-45 mmHg. In this study the aim was to review the applications of end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 monitoring in emergency department multiple databases were comprehensively searched with combination of following keywords. This is end-tidal CO2 ETCO2 which is normally 35-45 mm Hg.
Since problems with lungs are not common and gas exchange between alveoli and the blood is swift and effective. This is result of a slower expiration. Also called capnometry or capnography this noninvasive technique provides a breath-by-breath analysis and a continuous recording of ventilatory status.
End tidal CO 2 EtCO 2 monitoring is the fastest indicator of ventilatory compromise. Deeper slower alveoli are able to share their gas with the capnometer whereas previously that gas would have remained in the airway. Capnography can be used to measure end-tidal CO 2.
Measuring End Tidal CO2 Daltons Law. MmHg Relate to the air we breath.

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Exhaled Carbon Monoxide End Tidal Co2 And Peripheral Oxygen Saturation Download Table

End Tidal Capnography Can Be Useful For Detecting Diabetic Ketoacidosis Monitoring Copd Acep Now

3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram
End Tidal Co2 The Drummer Of The Vital Sign Band Pem4

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

Quantitative Waveform Capnography Acls Medical Training

Etco2 Valuable Vital Sign To Assess Perfusion The Airway Jedi
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationcapnography In The Ed Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education

The Impact Of Ventilation Rate On End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Level During Manual Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Resuscitation

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
Riding The Wave Of Capnography Understanding Etco2 Vetbloom Blog

End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Etco 2 Values Displayed Over The Monitors Download Scientific Diagram

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
Capnogram R Series Defibrillator Zoll Medical Uk

Exhaled Carbon Monoxide End Tidal Co2 And Peripheral Oxygen Saturation Download Table

Average Etco2 Kpa During Cpr In Patients With Or Without Rosc Download Scientific Diagram
